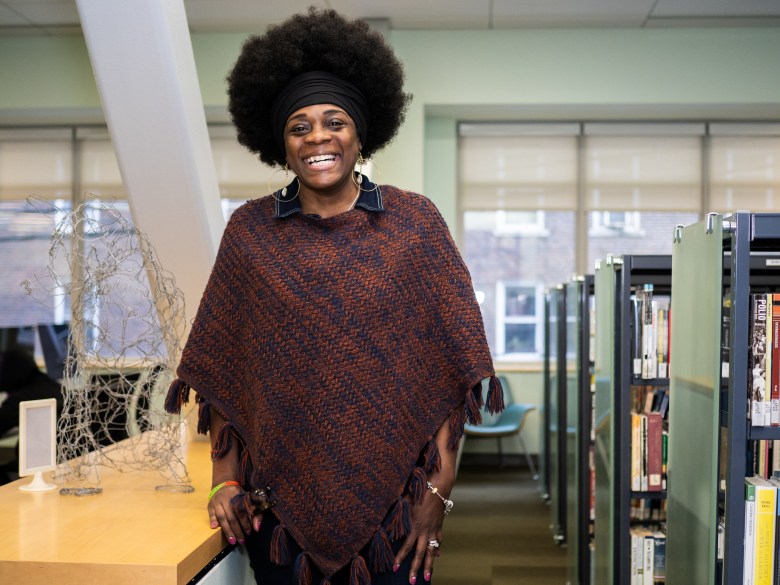
JERSEY CITY, N.J. — When Keischa Taylor sees fellow student-parents around her campus, she pulls them aside and gives them a hug.

“I tell them, ‘Don’t stop. You’ve got this. You didn’t come this far to stop. You’re not going to give up on yourself.’ ”
Taylor is exceedingly well qualified to offer this advice. She began her college education in her early 20s, balancing it with raising two sons and working retail jobs. And she just finished her bachelor’s degree last semester — at 53.
It’s a rare success story. Student-parents disproportionately give up before they reach the finish line. Fewer than four in 10 graduate with a degree within six years, compared to more than six in 10 other students.
Many have long had to rely on themselves and each other, as Taylor did, to make it through.
Now, however, student-parents are beginning to get new attention. A rule that took effect in California in July, for example, gives priority course registration at public universities and colleges to student-parents, who often need more scheduling flexibility than their classmates. New York State in September expanded the capacity of child care centers at community colleges by 200 spots; its campus child care facilities previously handled a total of 4,500 children, though most of those slots — as at many institutions with child care on campus, nationwide — went to faculty and staff.
Taylor put her sons in a Salvation Army daycare center when they were younger. “It’s a matter of paying for college, paying for the babysitter or sneaking them into class,” Taylor recalled, at Hudson County Community College, or HCCC, where she went before moving on to Rutgers University. Even though the community college is among the few that have improved their services for student-parents, she remembered asking herself, “How am I going to do this?”

Parents with children comprise a huge potential market for colleges and universities looking for ways to make up for the plummeting number of 18- to 24-year-olds and states’ growing need for workers to fill jobs requiring a college education. Many of these parents already have some college credits. More than a third of the 40.4 million adults who have gone to college but never finished have children under age 18, according to the Institute for Women’s Policy Research, or IWPR.
“If you want to serve adult learners, which colleges see as their solution to enrollment decline, you have to serve student-parents,” said Su Jin Jez, CEO of California Competes, a nonpartisan research organization that focuses on education and workforce policies.
Another reason student-parents are more visible now: The Covid-19 pandemic reminded Americans how hard it is to be a parent generally, never mind one who is juggling school on top of work and children.
Related: The hidden financial aid hurdle derailing college students
“A lot of the current energy has come from the focus on child care crises,” said Theresa Anderson, a principal research associate at the nonprofit research organization the Urban Institute. “Student-parents are at the intersection of that.”
There’s also new attention to the benefits for children of having parents who go to college.

“The greatest impact on a child’s likelihood to be successful is the education of their parents,” said Teresa Eckrich Sommer, a research professor at Northwestern University’s Institute for Policy Research.
Lori Barr dropped out of college when she got pregnant at 19, but went back as a mother and ultimately got a master’s degree. With her son, Minnesota Vikings linebacker Anthony Barr, she later co-founded a scholarship organization for single student-parents in California and Minnesota called Raise The Barr.
“Whatever we’re doing to support the parent directly impacts the child,” Barr said. “A parent can’t be well if the child’s not well, and vice versa.”
The effect works two ways, Sommer said. In a study she co-authored of an unusual program that gives college scholarships to both high school students and their parents in Toledo, Ohio, the Institute for Policy Research found that students and parents alike performed at or above average, despite what Sommer noted were financial challenges and limited academic preparation.
“Call it mutual motivation. The children helped the parents with technical issues. The parents helped the children with time management,” she said. “We think of kids as a barrier to student success. We have to turn that on its head. Kids are a primary motivator to student success.”
Tayla Easterla was enrolled at a community college near Sacramento, California, when her daughter was born prematurely four years ago; she took her midterms and finals in the neonatal intensive care unit. “I just found that motherly drive somewhere deep inside,” said Easterla, 27, who now is majoring in business administration at California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo.
Krystle Pale is about to get her bachelor’s degree from the University of California, Santa Cruz. When she looks at her children who live with her, who are 5, 7, 12 and 13, “I want better for them. I just want them to have a better life,” said Pale, choking up.
Sydney Riester, of Rochester, Minnesota, who is about to earn her dental assistant associate degree, also said her children — ages 3, 6 and 7 — were foremost in her planning. “These kids need me, and I need to get this done for them,” Riester said.
Related: ‘We’re from the university and we’re here to help’
There’s a surprising lack of information about whether students in college have dependent children. Most institutions never ask. That is also slowly changing. California, Michigan, Oregon and Illinois have passed legislation since 2020 requiring that public colleges and universities track whether their students are also parents. A similar federal measure is pending in Congress.
“Ask community college presidents what percentage of their students are parents, and they’ll say, ‘That’s a really good question. I’ll get back to you,’ ” said Marjorie Sims, managing director of Ascend at the Aspen Institute, one of a growing number of research, policy and advocacy organizations focusing on student-parents.
Nearly one in four undergraduate and nearly one in three graduate students, or more than 5.4 million people, are parents, the Urban Institute estimates. More than half have children under age 6, according to the IWPR.

Seventy percent of student-parents are women. Fifty-one percent are Black, Hispanic or Native American. Student mothers are more likely to be single, while student fathers are more likely to be married.
Among student-parents who go to college but drop out, cost and conflicts with work are the most-stated reasons, various research shows; 70 percent have trouble affording food and housing, according to the Hope Center for College, Community, and Justice at Temple University.
Student financial aid is based on an estimated cost of attendance that includes tuition, fees, books, supplies, transportation and living expenses, but not expenses related to raising a child. The out-of-pocket cost of attending a public university or college for a low-income parent can be two to five times higher than for a low-income student without children, according to the advocacy group The Education Trust.
A student-parent would have to work 52 hours a week, on average, to cover both child care and tuition at a public university or college, EdTrust says. A separate analysis by California Competes found that students in that state who have children pay $7,592 per child a year more for their educations and related expenses than their classmates who don’t have kids.
But “when they apply for financial aid, they get financial aid packages as if they don’t have children. It’s ludicrous,” said Jez, at California Competes.

Forty-five percent of student-parents who dropped out cited their need to provide child care as a significant cause, a survey released in February found. Yet the number of colleges and universities with on-campus child care has been dropping steadily, from 1,115 in 2012 to 824 today, federal data shows. That’s a decline of 291 institutions, or 26 percent.
Fewer than four in 10 public and fewer than one in 10 private, nonprofit colleges and universities have on-campus child care for students, an analysis by the think tank New America found. Ninety-five percent of those campus child care centers that existed in 2016 — the most recent year for which data is available — had waiting lists, and the number of children on the average waiting list was 82, according to the IWPR. Other students couldn’t afford the cost.
Related: When a Hawaii college sets up shop in Las Vegas: Universities chase students wherever they are
“Colleges and universities that enroll student-parents should be committed to serving their needs,” said Christopher Nellum, executive director at EdTrust-West and himself the son of a student-mother who ultimately dropped out and enlisted in the military, finding it was easier to be a parent there than at a community college. “It’s almost willful neglect to be accepting their tuition dollars and financial aid dollars and not helping them succeed.”
Even where child care is available and spots are open, it’s often too expensive for students to manage. More than two-thirds of student-parents in Washington State said they couldn’t afford child care, a state survey last year found. About half of student-parents nationwide rely entirely on relatives for child care.

Hannah Allen, who goes to HCCC, gets up at 5 a.m. to get her three kids ready for the day — first the 4-year-old, then the 6-year-old, then the 8-year-old. “I go down the line,” she said. Her schedule is so tight, she has a calendar on her refrigerator and another on the wall.
She can’t drop off her children at school or daycare earlier than 8:30 or pick them up later than 5. “When my kids are in school is when I do as much as I can.” She calls her school days “first shift,” while her time at home at night is “second shift.”
“First you put your kids, then you put your jobs, then you put your school and last you put yourself,” said Allen. “You have to push yourself,” she said, starting to cry softly. “Sometimes you think, ‘I can’t do it.’ ”

There is a little-noticed federal grant program to help low-income student-parents pay for child care: Child Care Access Means Parents in School, or CCAMPIS. Last year CCAMPIS was allocated about $84 million; the Government Accountability Office found that student-parents who got CCAMPIS’s subsidies were more likely to stay in school than students generally. But there were more students on the waiting list for it than received aid. A Democratic proposal in the Senate to significantly increase funding for the program has gone nowhere.
The Association of Community College Trustees, or ACCT, is pressing member colleges to make cheap or free space available for Head Start centers on their campuses in the next five years. Fewer than 100 of the nation’s 1,303 two-year colleges — where more than 40 percent of student-parents go — have them now, the ACCT says.
Related: Aging states to college graduates: We’ll pay you to stay
These things are a start, but much more is needed, said Chastity Lord, president and CEO of the Jeremiah Program, which provides students who are single mothers with coaching, child care and housing. “When your child is sick, what are you going to do with them? It becomes insurmountable. Imagine if we had emergency funding for backup child care.”

Jen Charles struggled with child care as she tried to earn a degree and become a social worker from the time she was 19, when she had a son who was born with disabilities. He was followed by a daughter. Charles was also working, as an administrative assistant and, later, a paralegal.
“When things were going smoothly, I would enroll for one class and say, ‘I’m going to get through this,’ ” she said. But it proved too much. And even though Charles, now 49, got an information technology certification last year through the continuing education arm of HCCC, earning a full-fledged degree “became kind of an extinguished dream.”
As important as an education was to her, she said, “your priority becomes being able to sustain your family — their well-being, their needs being met, a roof, food. All of these other things take precedence. And where in there do you fit your papers that are due, or studying for your quiz? Is that at 10 o’clock at night, when you’re exhausted?”
Just across the Hudson River from Manhattan, HCCC has steadily added programs to support the parents among its 20,000 students. It has set aside “family-friendly” spaces in libraries and lounges and holds events for parents with kids, including movie nights, barbecues, trick-or-treating and a holiday tree-lighting ceremony. There’s a food pantry with meals prepared by the students in the college’s culinary program.
Student-parents get to register first for courses. College staff help with applications to public benefit programs. Lactation rooms are planned. And there are longer-range conversations about putting a child care center in a new 11-story campus building scheduled to open in 2026.

The college’s 20,000 students are largely poor and the first in their families to go to college, said Christopher Reber, HCCC’s president, and many are not native English speakers. Ninety-four percent qualify for financial aid. Having children, Reber said, “adds insurmountable challenges to that list of insurmountable challenges.”
There’s an even more immediate motivation for the two-year college to support its student-parents. It graduates only 17 percent of students, even within three years, which is among the lowest proportions in the state.
“If a student doesn’t know where their next meal is coming from, it doesn’t matter how much academic support you offer — the student is not going to succeed,” said Reber, in his office overlooking downtown Jersey City.
Related: One college finds a way to get students to degrees more quickly, simply and cheaply
With a grant it got in January from the Aspen Institute’s Ascend, HCCC is expanding its work with the housing authority in Jersey City to help student-parents there enroll in and complete job-focused certificate programs in fields such as bookkeeping and data analytics, hiring a coordinator to work with them and appointing an advisory committee made up of student-parents.
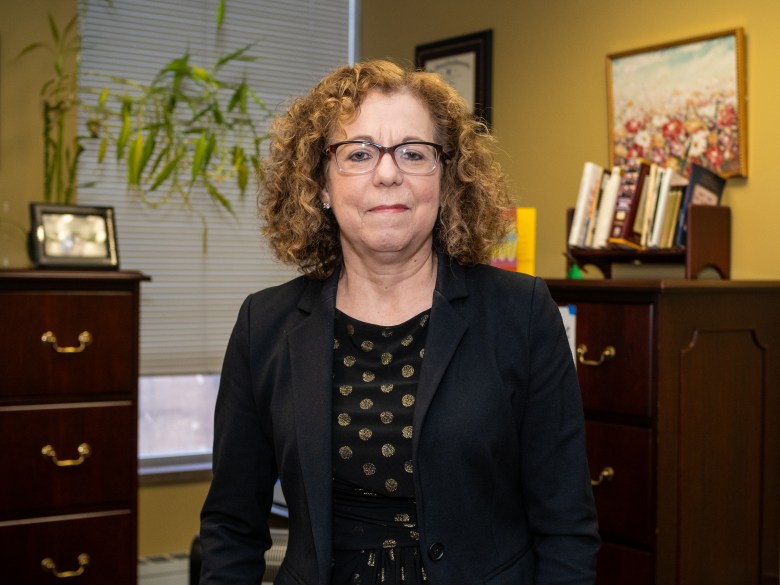

It can be hard to win the trust of student-parents, said Lori Margolin, HCCC’s associate vice president for continuing education and workforce development. “Either they’ve tried before and it didn’t work out, so they’re reluctant to go back, or it’s too much of an unknown. ‘Do they care that I have children and I’m not going to be able to take classes at these times?’ ”
Like other schools, HCCC had what Reber called “Neanderthal” rules for student-parents. They weren’t allowed to bring their kids to campus, for example.
“I remember one student, a single mother, relying on parents and friends to watch her baby. The only time she could study was late at night [in the library], but the library said no.”
That rule was dropped, with more changes planned. A new program will reward student-parents with financial stipends for doing things such as registering early and researching child care options, said Lisa Dougherty, senior vice president for student affairs and enrollment at HCCC.
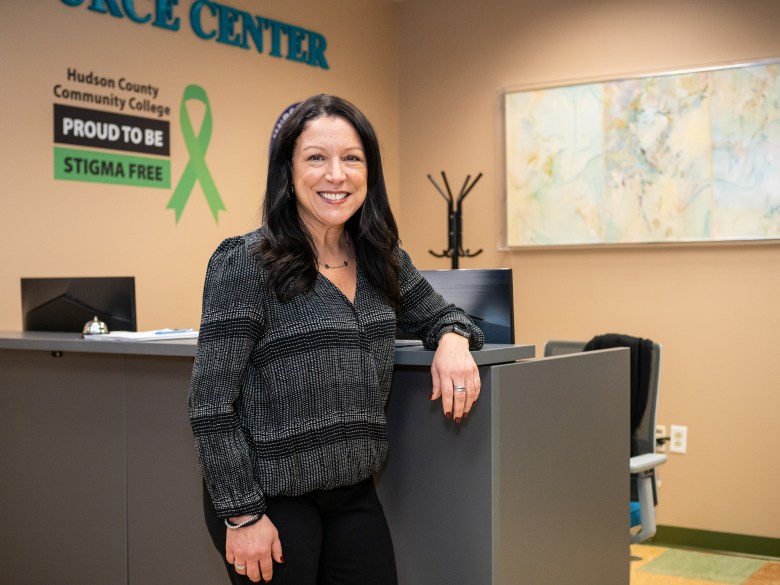

A few other colleges and universities have programs designed for student-parents. Misericordia University in Dallas, Pennsylvania provides free housing for up to four years for up to 18 single mothers, who also get academic support and tutoring, priority for on-campus jobs and access to a children’s library and sports facilities.
At Wilson College in Pennsylvania, up to 12 single parents annually are awarded grants for on-campus housing and for child care, and their children can eat in the campus dining hall for free.
St. Catherine University in Minnesota subsidizes child care for eligible student-parents and has child-friendly study rooms.
And Howard Community College in Maryland, whose president was once a student-parent, provides mentorship, peer support, career counseling, financial assistance and a family study room in the library.
“That may not seem like a big deal, but those are the messages that say, ‘You belong here, too,’ ” Lord said.
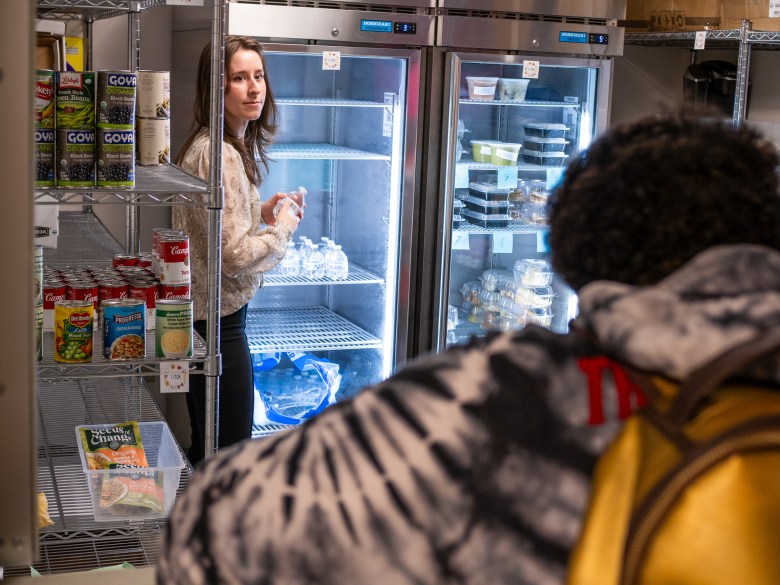

These efforts have so far helped a small number of students. Forty single mothers have graduated from the Misericordia program since it was launched more than 20 years ago, for instance.
Some of the obstacles for student-parents are hard to measure, said Jessica Pelton, who finished community college after having a daughter at age 20 and ultimately graduated from the University of Michigan, where her husband also was enrolled.
“You’re typically isolated and alone,” said Pelton. “I just kind of stuck to myself.”
She would often miss out on nighttime study groups with classmates who lived on campus. “Their priorities are not to go home, make dinner and put their kid to bed. We don’t have the option to go party. We’re not here on our parents’ money. We’re paying our own way.”
Some faculty offered to let her bring her daughter to class, she said. “It really meant a lot to me, because it made me feel like a part of campus.”
Finding fellow student-parents helps, too, said Omonie Richardson, 22, who is going to college online to become a midwife while raising her 1-year-old son and working as a chiropractic assistant 35 hours a week in Fargo, North Dakota.
“I felt very isolated before I found a group of other single moms,” she said. “If we had the understanding and support in place, a lot more parents would be ready to pursue their educations and not feel like it’s unattainable.”
This story about student-parents was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for our higher education newsletter. Listen to our higher education podcast.



